The Commission has determined that extension cords (for indoor and outdoor use) that do not contain one or more applicable readily observable safety characteristics (minimum wire size; sufficient strain relief; proper polarization; proper continuity; outlet covers (for indoor cords); and jacketed cords (for outdoor cords) present a risk of electrical shock or fire and constitute a substantial product hazard.
The Commission’s determination has certain consequences described below. Notably, a product on the “substantial product hazard” list is subject to the mandatory reporting requirements of section 15(b) of the CPSA. 15 U.S.C. 2064(b).
Extension cords (see figure 1) are used for extending the electricity supply of an electrical outlet or receptacle to a portable corded appliance or device, such as a toaster, a lamp, a television, or a leaf blower. The rule applies to extension cords that are equipped with National Electrical Manufacturer Association (“NEMA”) 1-15, 5-15 and 5-20 fittings (see figure 2), and that are intended for indoor use only, or for both indoor and outdoor use. The Commission refers to cords intended for indoor use only as “indoor cords” and to cords intended for both indoor and outdoor use as “outdoor cords.” The term “extension cord” does not include detachable power supply cords, appliance cords, power strips and taps, and adaptor cords supplied with outdoor tools and yard equipment (see figure 3). (Extension cords have receptacles or outlets molded into the cord itself, whereas power strips and taps have flexible cord but receptacles or outlets are not molded into the cord itself. Power strips and taps covered by a voluntary industry consensus, the Standard for Current Taps and Adapters, UL 498A)
Figure 1
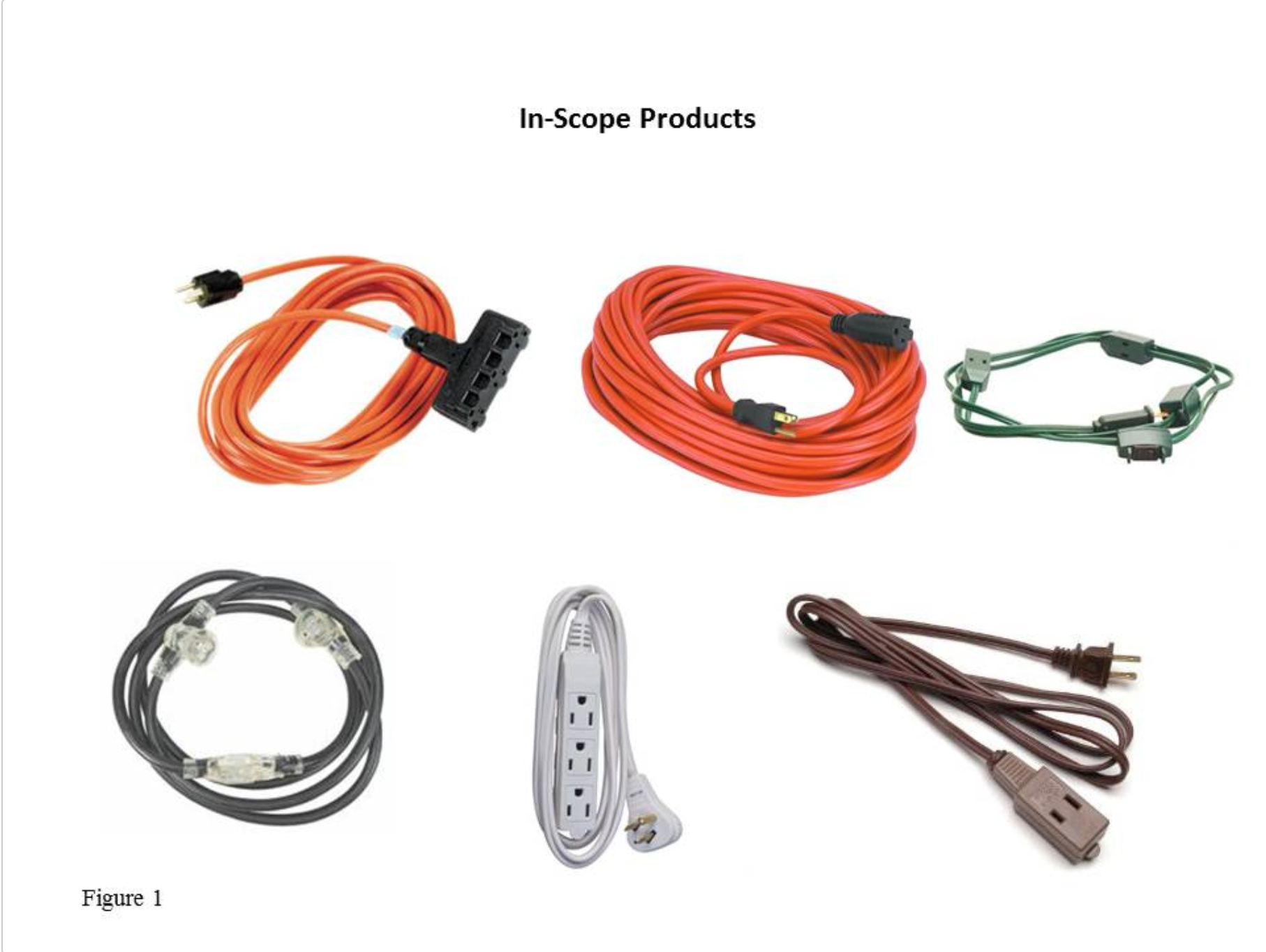

Figure 2

Figure 3

All products within the scope of the rule are covered by UL 817.
The following table provides a non-exhaustive list of examples of extension cords that fall within and outside the scope of the rule.
In Scope: Household extension cords, factory-assembled,
120 volts AC, including:
- Indoor or general-use extension cords (also known as cord sets), including seasonal indoor extension cords (which are designed to be used for only limited time period)
- Outdoor extension cords (also known as cord sets)
Out of Scope:
- Detachable power cords, either with appliance or other nonstandard plugs (e.g., accompanying electronic or other electrically powered items), or with fittings of different configurations (e.g., a clothes washer replacement cord with a plug at one end and individual wire terminals at the other end)
- Unassembled components, such as flexible cord or fittings, which may be assembled into extension cords or installed in permanent branch circuit wiring systems
- Cord sets intended for use with non-branch-circuit household current, i.e., greater or less than nominal 120 volts AC (e.g., for use with 220 volt appliances, or for 15-50 ampere/125-–250-volt recreational vehicles)
- Power strips, power taps, and surge protectors
What are the requirements of UL 817-2014?
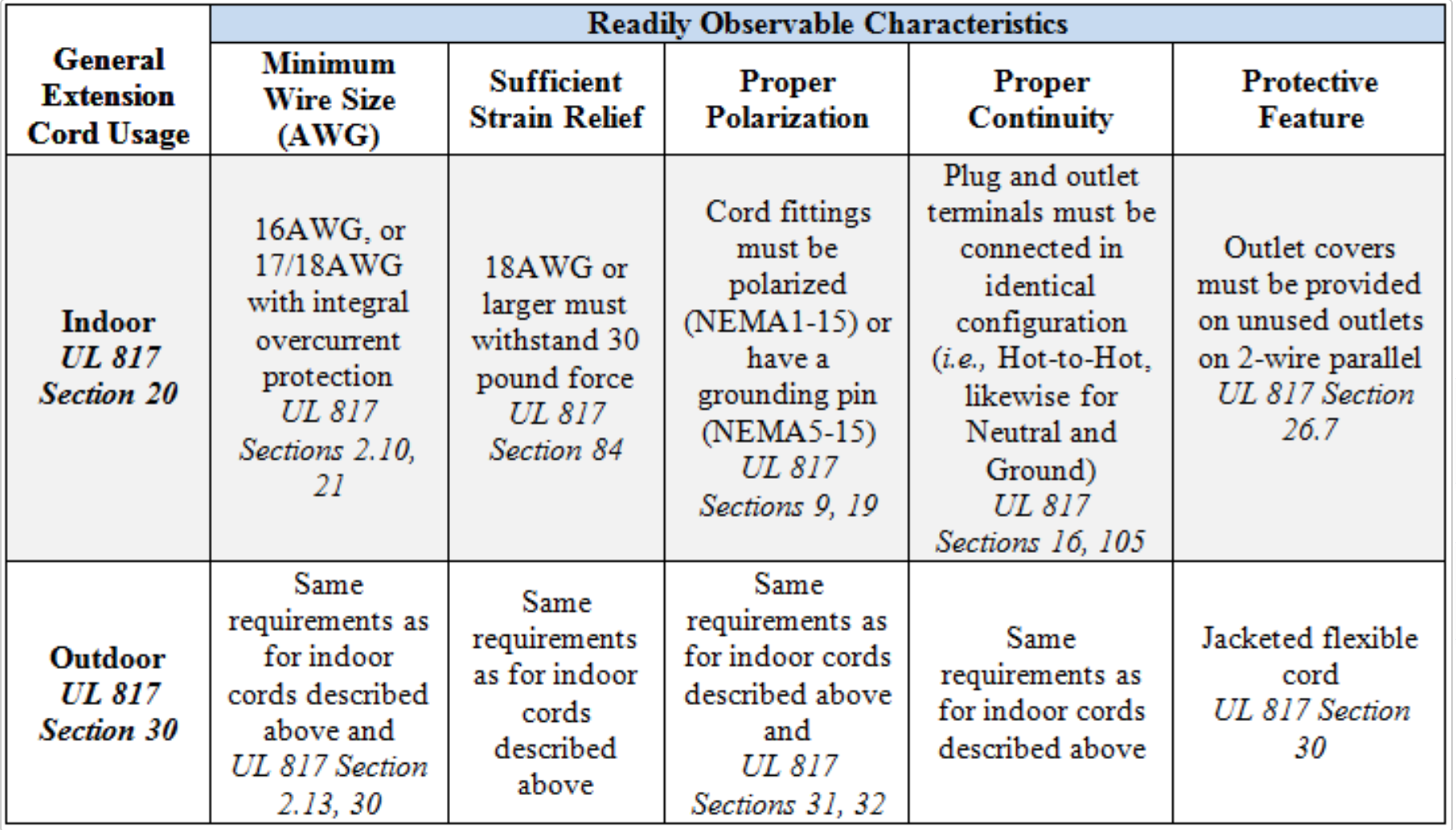
In general, sections 2, 9, 16, 19, 20, 21, 26, 30, 31, 32, 84, and 105 of UL 817 set forth the requirements for the readily observable characteristics specified in the rule: minimum wire size; sufficient strain relief; proper polarization; proper continuity; outlet covers (for indoor cords); and jacketed cords (for outdoor cords). The presence of these characteristics reduces the risk of electrical shock or fire.
Table: Readily Observable Characteristics for Extension Cords
Please see the Commission’s final rule (80 FR 44262 (July 27, 2015)) for more details and review a copy of UL 817-2014.
Additionally, one characteristic (outlet covers) applies to 2-wire indoor extension cords, and one characteristic (jacketed cord) applies to outdoor extension cords. Thus, 2-wire indoor and all outdoor extension cords would each be required to exhibit five readily observable characteristics described in UL 817. If one or more applicable characteristics are missing, the product presents a substantial product hazard under section 15(a)(2) of the CPSA.
Although a 15(j) rule does not establish a consumer product safety standard, placing a consumer product on this substantial product hazard list has certain consequences. A product on the “substantial product hazard” list is subject to the reporting requirements of section 15(b) of the CPSA. 15 U.S.C. 2064(b). A manufacturer who fails to report a substantial product hazard to the Commission in accordance with CPSC requirements at [cite CFR] is subject to civil penalties under section 20 of the CPSA and possibly is subject to criminal penalties under section 21 of the CPSA. 15 U.S.C. 2069, 2070. A product that is, or contains, a substantial product hazard, is subject to corrective action under section 15(c) and (d) of the CPSA. 15 U.S.C. 2064(c), (d). Thus, the Commission can order the manufacturer, distributor, or retailer of the product to offer to repair or replace the product, or to refund the purchase price to the consumer. Finally, a product on the “substantial product hazard” list that is offered for import into the United States must be refused admission into the United States under section 17(a) of the CPSA. 15 U.S.C. 2066(a).
- Office of Compliance (for specific enforcement inquires): e-mail: section15@cpsc.gov; telephone: (800) 638-2772.
- Small Business Ombudsman (for general assistance understanding and complying with CPSC regulations): e-mail: Please use our Contact Form, which is the best way to get a fast response; telephone: (888) 531-9070.


